Cryptocurrency and Bitcoin
Bitcoin protocol
- Based on secret key, i.e. each coin may be paired with a SK
- Throughput limitation: 1M bytes/block (10 min); >250 bytes/Tx; 7 Txs/sec [VISA: 2K-10K Txs/sec; PayPal: 50-100 Txs/sec]
- Cryptographic limits: only one algo (ECDSA/P256); hard-coded hash functions
- Changes that require a “hard-fork” update (not accepted by the community):
- New op codes
- Chenges to size limits
- Changes to mining rate
- Many small bug fixes e.g. TODO
Bitcoin P2P network
- Ad-hoc protocol (runs on TCP port 8333)
- Ad-hoc network with random topology
- All nodes are equal
- New nodes can join at any time
- Forget non-responding nodes after 3 hr
- Node relays Tx if:
- Tx is valid with current block chain
- script matches a whitelist
- Haven`t seen before
- Doesn’t conflict with others it has already realyed
- Race conditions are natural:
- Default behavior: accept what came first
- Network position matters
- Miners may implement other logic
- Thin/SVP clients validate only a part of the blockchain (just to verify incoming payment) can perform even on a mobile phone (requires 1000 times less memory than the whole blockchain)
Bitcoin wallet
- Typically split into hot and cold ends, where hot is an online wallet (aka cash) and cold – is a offline permament storage
- paper wallet
- secret splitting == multi-sig
- in case K-out-of-N splitting each part will have size equal to the secret
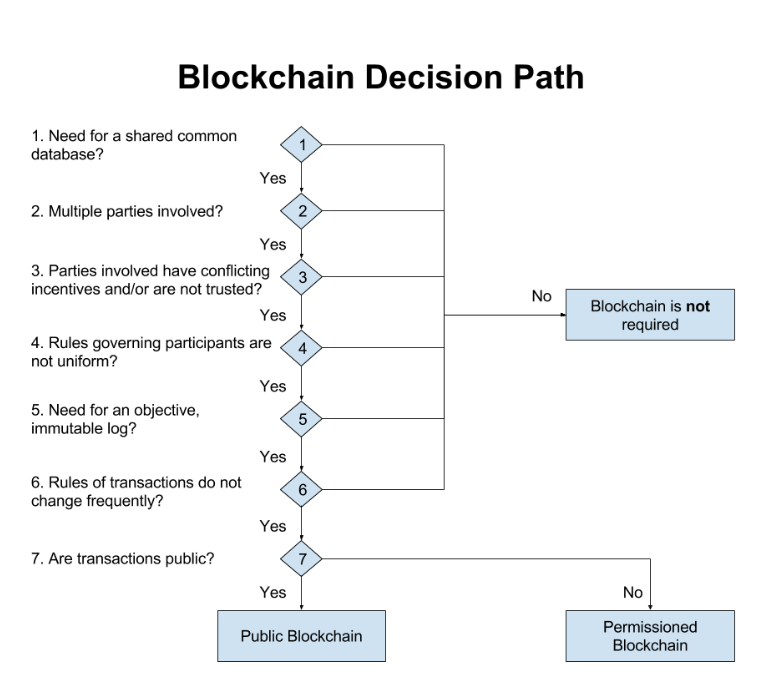
Bitcoin for Business (aka Blockchain platform)
- Identity over anonymity
- Selective endorsment over Proof-of-Work
- Assets over cryptocurrency
- Requirements for a blockcahin in a business environment
- Shared ledegr (permissions i.e. participant sees only what is allowed)
- Privacy (Txs must be authenticated, cryptography)
- Smart contract (encoded in a programming language, verifiable, signed)
- Trust (consensus, provenance, immutability and finality)
- Developer consideration: integration with existing systems:
- via events
- via direct call (may require transformation)
- blockchain platform may call exeisting system directly (cautions required e.g. constanctly changed value must be treated carefully in this case)
- Performance:
- the amount if shared data
- number and location of peers
- latency and throughput
- batching characteristics (how many Txs submitted to a block)
- Security:
- type of the data being shared and with whom
- how is identity achieved
- confidentiallity of Tx queries
- who verifies (endorses) Txs
- Resiliency
- resource failure
- malicious activity
- non-determenistic
More content is coming soon…